Reed Switch Tutorial for Arduino, ESP8266 and ESP32
In this tutorial we learn how to build our own security system for doors or windows with a reed switch.
Reed switches are magnetically-actuated electrical switches which switch based on a magnetic field. If magnetic field through a magnet or a strong electrical current is present to the reed switch, the connection inside the switch closes and the circuit is closed so that a current flow is present.
Otherwise if there is no magnetic field, the switch remains open.
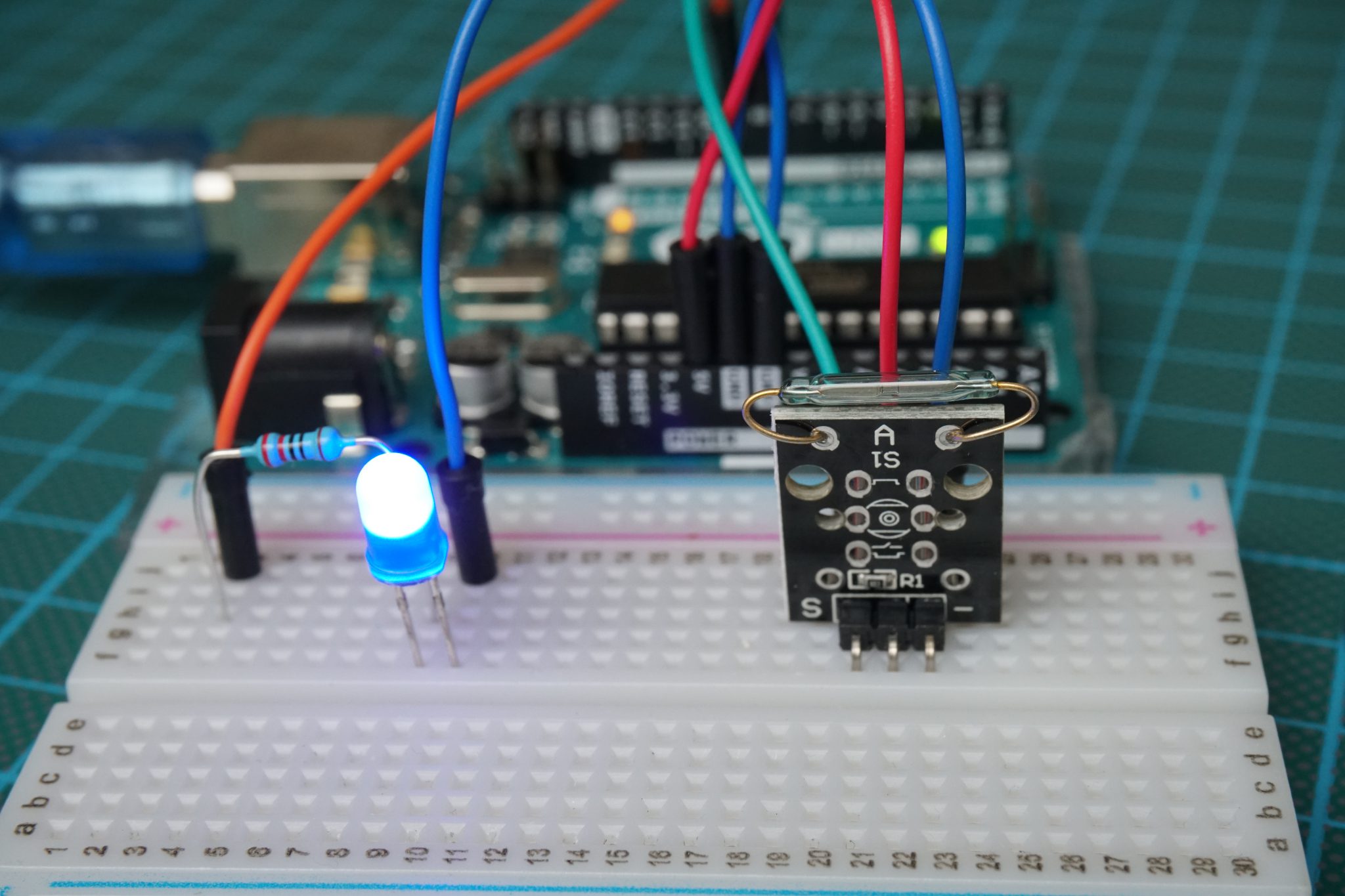
Table of Contents
Reed Switch vs Magnetic Hall Sensor
The reed switch is not the only electrical device with can be used as a magnetic switch. There is also the magnetic hall sensor. For some use cases there is no difference if you use a reed switch or a magnetic hall sensor. But a big difference is how the direction of the magnetic field has to be in order to use the magnetic switch. In the following table you find the comparison between the two magnetic switches with the advantages and disadvantage and also how the magnet – sensor orientation has to be.
If you are interested in the (magnetic) hall sensors, I wrote a complete tutorial for this as well.
Use of the Reed Switch
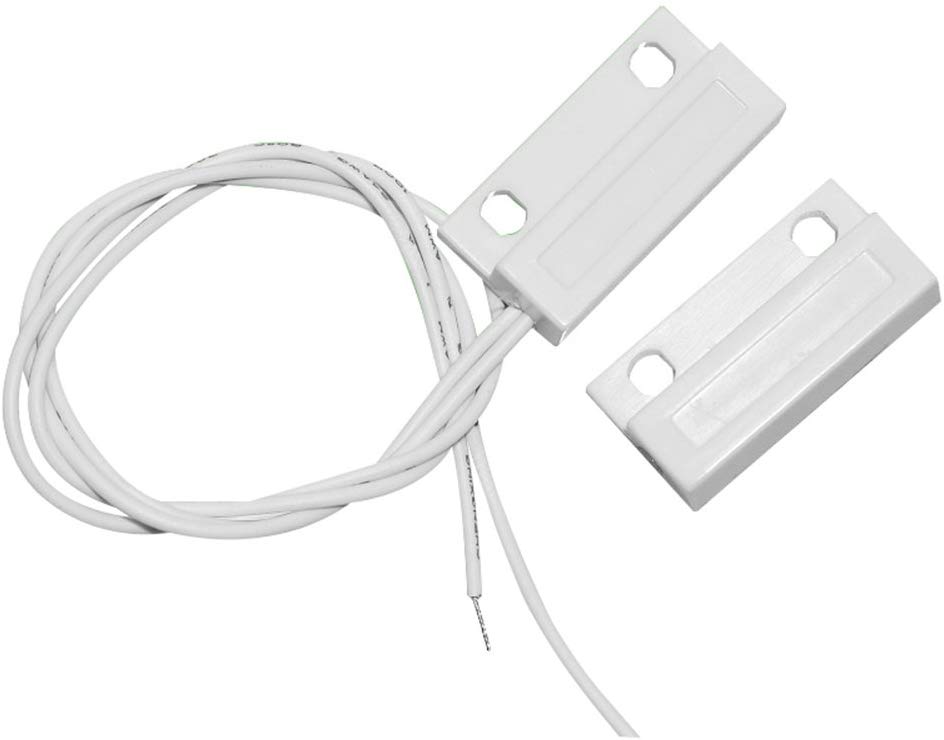
A very common application of reed switches is to detect if a door or window is open or closed. Therefore you have one side of the sensor with the reed switch and an other side with the magnet like you can see in right picture.
Because the magnetic field is directed and therefore has a direction, the position and angle between the reed switch and the external magnet is important. There are two opposite scenarios which are also seen the in two following pictures. On the left side the magnet is parallel to the reed switch and in the right picture, the magnet is perpendicular to the magnetic switch.
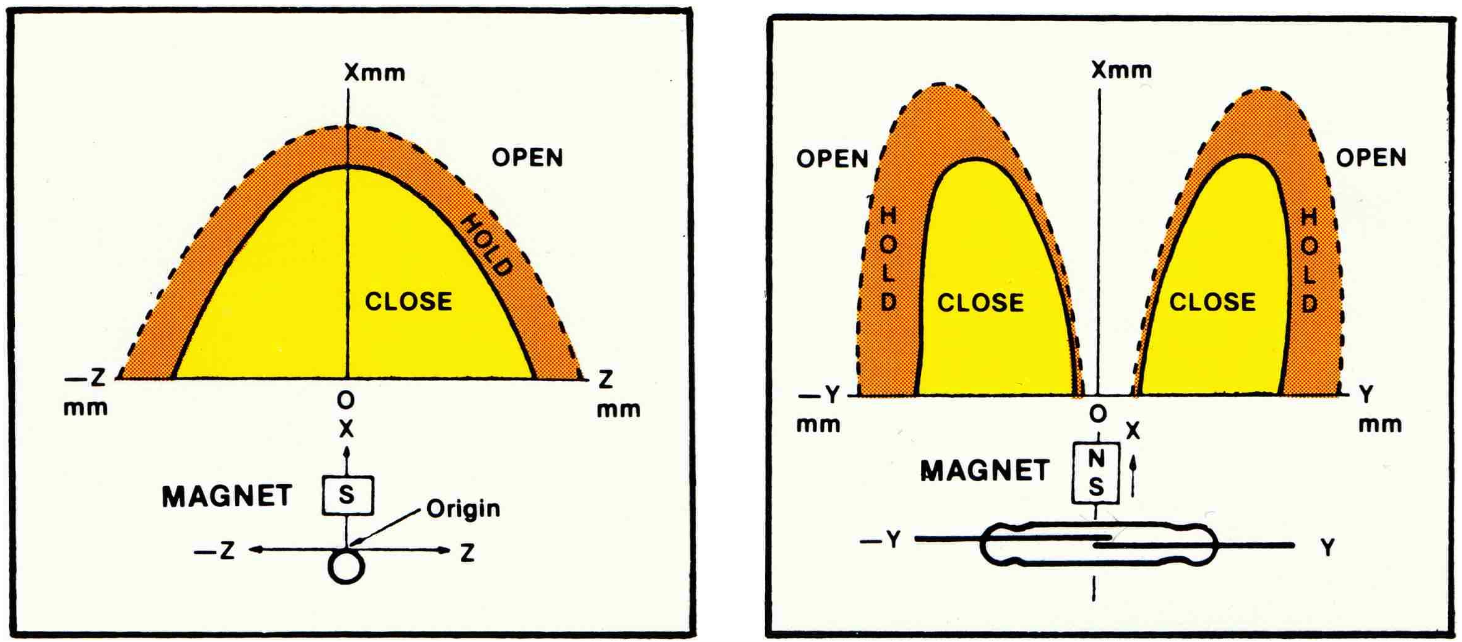
Magnet is parallel to reed switch
This is the perfect setup that you also find in the door or window detection use case because the build up magnetic field is parabolic.
Magnet is perpendicular to reed switch
In this setup the magnetic field has a dead zone in the middle of the reed switch. Therefor do not use the magnet and reed switch in a perpendicular setup.
There are two reed switch modules on the market. The KY-025 and the KY-021. The following table compares the technical data sheet between these two reed modules.
In the following sections, we want to measure the magnetic field with both, the KY-025 and the KY-021. Therefore we take a look in the wiring between the reed switch and the microcontroller. After the wiring is done we create a sketch to measure the magnetic field. Because the KY-021 has only a digital output, we can not measure how strong the magnetic field is, only if a predefined threshold through the 10kΩ resistor is exceeded.
With the KY-025 we gain much better flexibility, because we are able to measure the strength of the magnetic field with the analog output and are able to define the threshold with the potentiometer for our self.
The following table gives you an overview of all components and parts that I used for this tutorial. I get commissions for purchases made through links in this table.
KY-025 Read Analog and Digital Values
In the following example we want to read the analog and digital value of the KY-025 reed switch.
With the analog connection we are able to get the status of the magnetic switch but can not measure exactly how strong the magnetic field is because the switch is very fast. We want to display the switch cycles to the serial output of the Arduino IDE to see that the analog values do not have any information of the strength of the magnetic field and therefore provide not more information than the digital value.
The KY-025 has a build in potentiometer to set the threshold for the digital value to change between 0 and 1 based on the analog value. The digital value is
- 0 for the threshold is not exceeded (build in LED is off), because the reed switch is open
- 1 for the threshold is exceeded (build in LED is turned on), because the reed switch is closed
The setup of the threshold is very hard because the sampling rate of the serial communication is not very high. Therefore we can use an oscilloscope with a high sampling rate connected to the analog pin to see the current voltage of the analog pin that is changing when the potentiometer is changed.
To stimulate the reed switch I use a magnet with 2 sides (north and south).
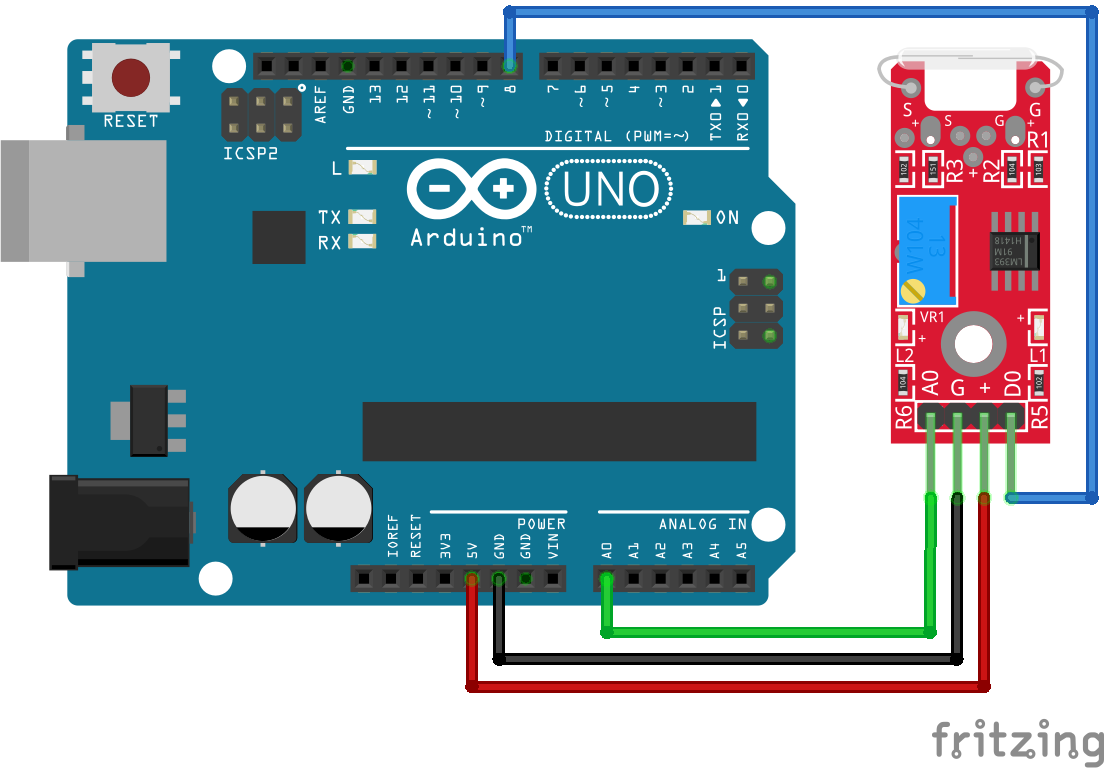
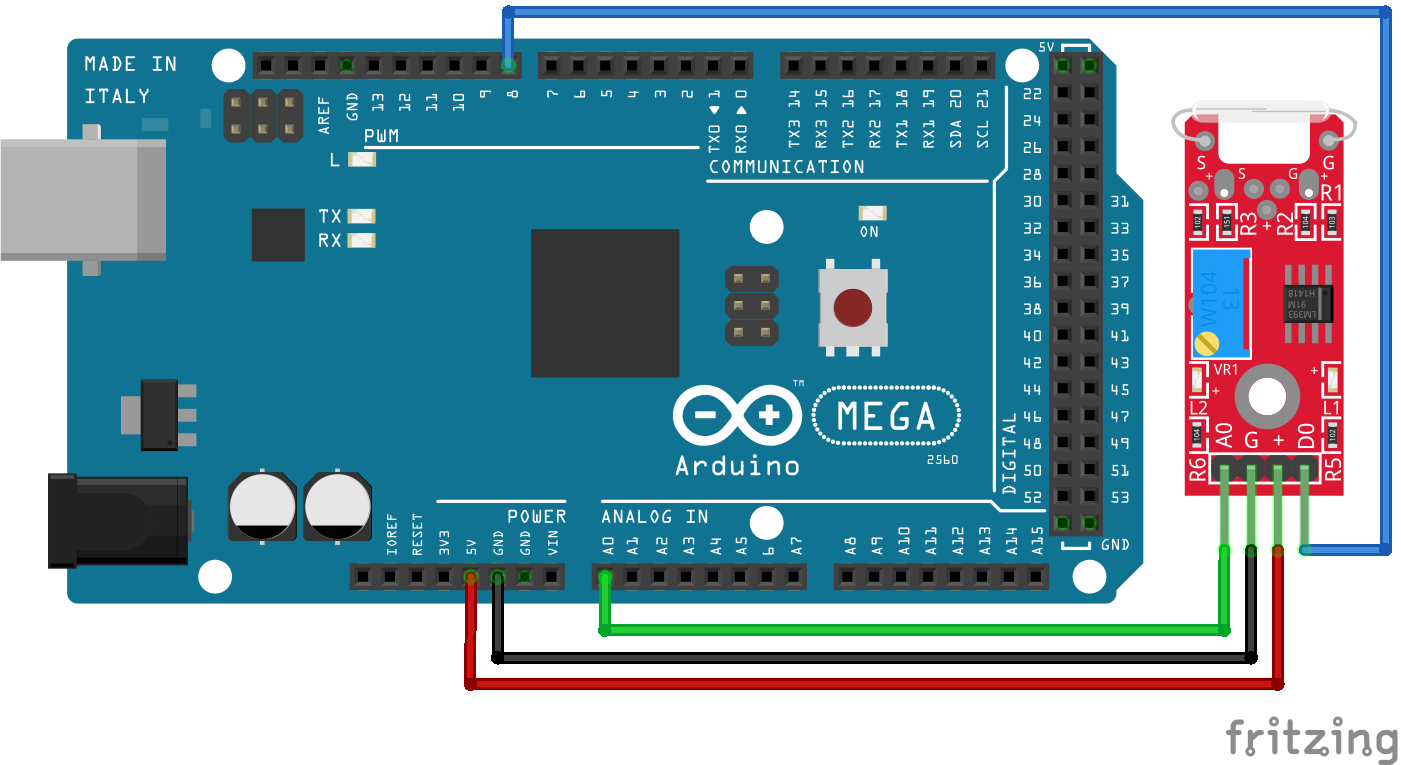
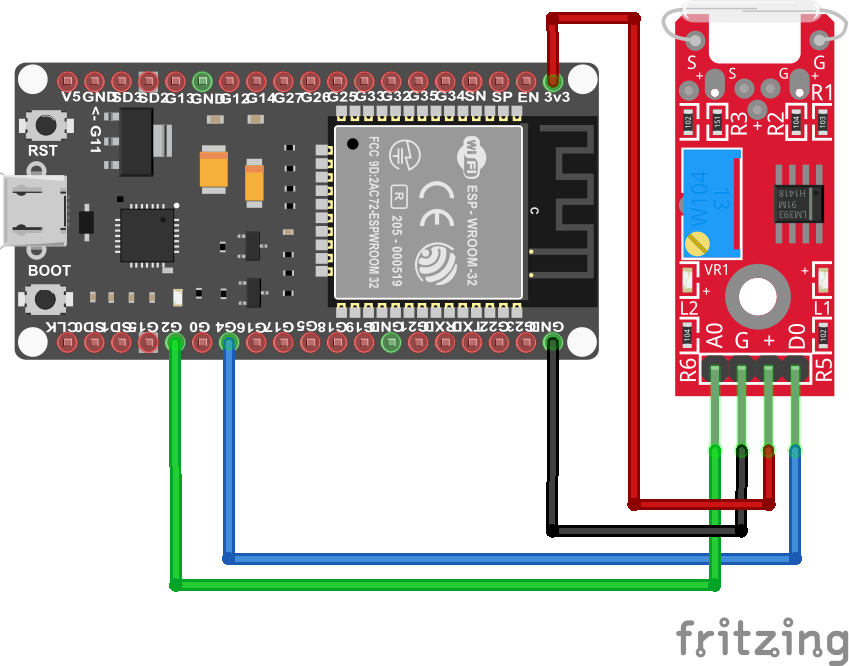
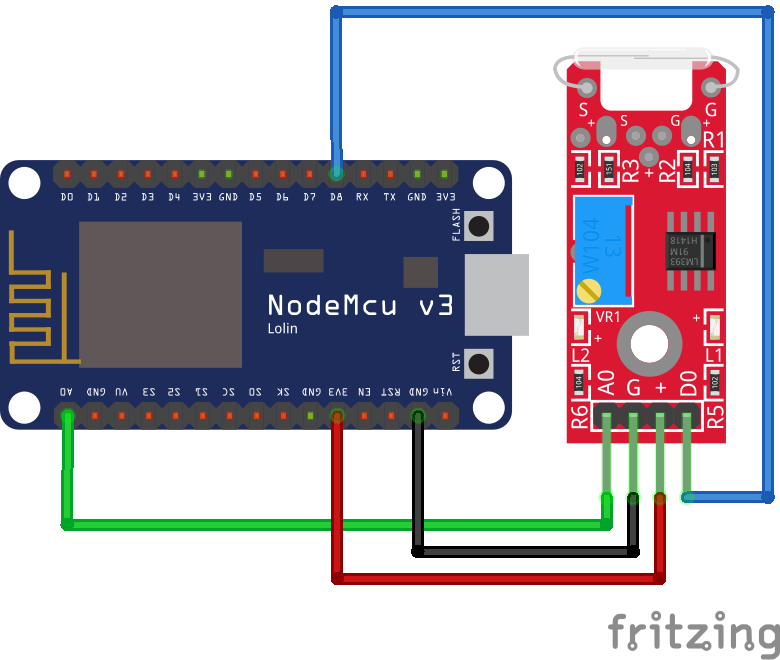
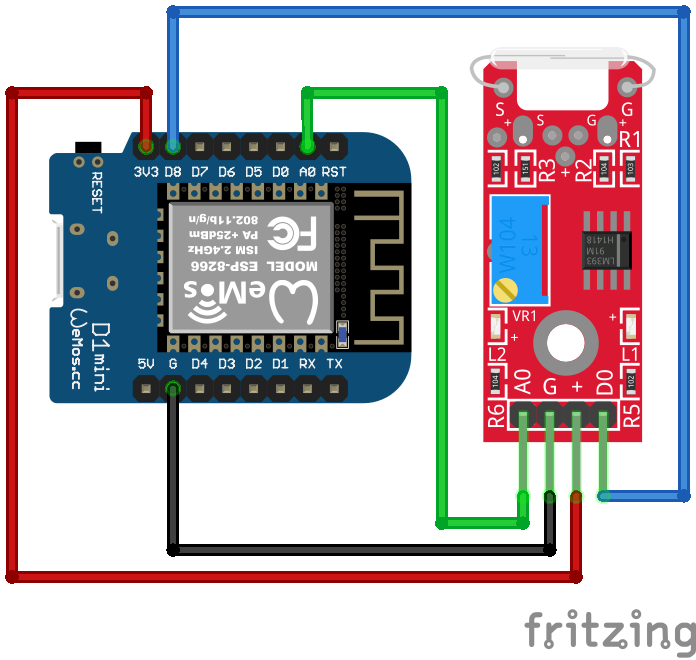
The following pictures show the wiring between the KY-025 and the Arduino, ESP8266 or ESP32 microcontroller.
After we wire the KY-025 and the microcontroller, we can create the Arduino script that displays the analog and digital value of the reed switch. We go step by step over the program code and I explain what we are doing.
// for Arduino microcontroller
int analogPin = A0;
int digitalPin = 8;
// for ESP8266 microcontroller
//int analogPin = A0;
//int digitalPin = D8;
// for ESP32 microcontroller
//int analogPin = 4;
//int digitalPin = 2;
void setup() {
pinMode(analogPin, INPUT);
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int analogVal = analogRead(analogPin);
int digitalVal = digitalRead(digitalPin);
Serial.print(analogVal);
Serial.print(" - ");
Serial.println(digitalVal);
delay(100);
} At the beginning of the script we have to define the pins that connect the microcontroller with the KY-025 module. Because this script can be used for Arduino, ESP8266 and ESP32 microcontroller, if defined all connections but commented the lines for the ESP8266 and ESP32. Therefore if you want to use the script for an ESP microcontroller board, you have to comment the Arduino lines and uncomment the desired ESP lines.
In the setup function, we define the pin mode of the two connection pins as inputs, because we want to read the sensor data of the reed switch. Also we set the baud rate of the serial connection to the PC to 9600 to view the sensor values in the Arduino IDE. The baud rate must match the baud rate of the serial monitor in the Arduino IDE.
In the loop function we read the analog value from the previous defined analog pin and save the analog sensor value as integer variable. We do the same for the digital value but read of cause the digital value from the digital pin.
Now we print both value to the serial monitor and include a short delay of 0.1 seconds before we read the next sensor values in the next iteration of the loop function.
The following videos and pictures show the results of this example:
- KY-025 Analog Measurement in the Serial Plotter of the Arduino IDE
- KY-025 Digital Measurement in the Serial Monitor of the Arduino IDE
- KY-025 Visualize the influence of the potentiometer on the analog sensor value, measured with an oscilloscope
KY-025 Analog Measurement
KY-025 Digital Measurement

KY-025 Visualize the influence of the potentiometer on the analog sensor value
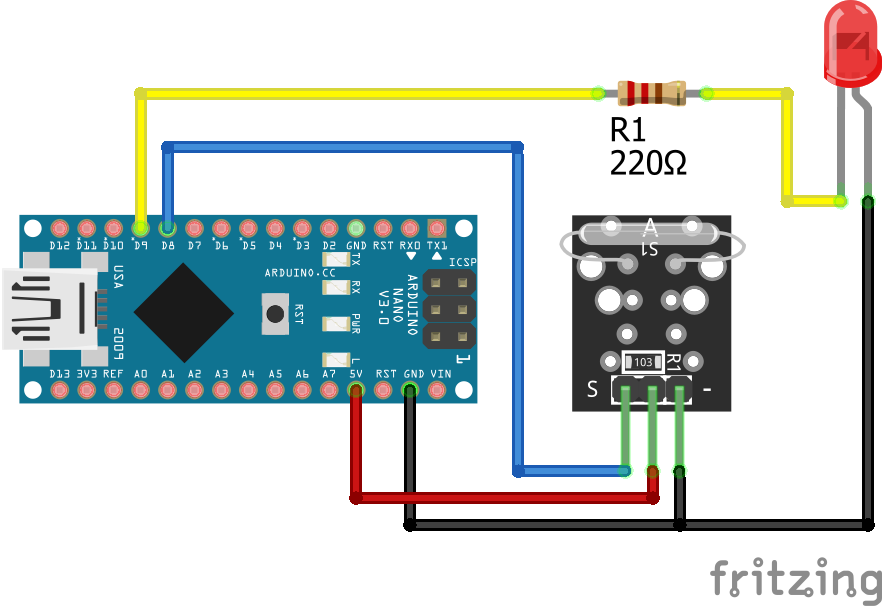
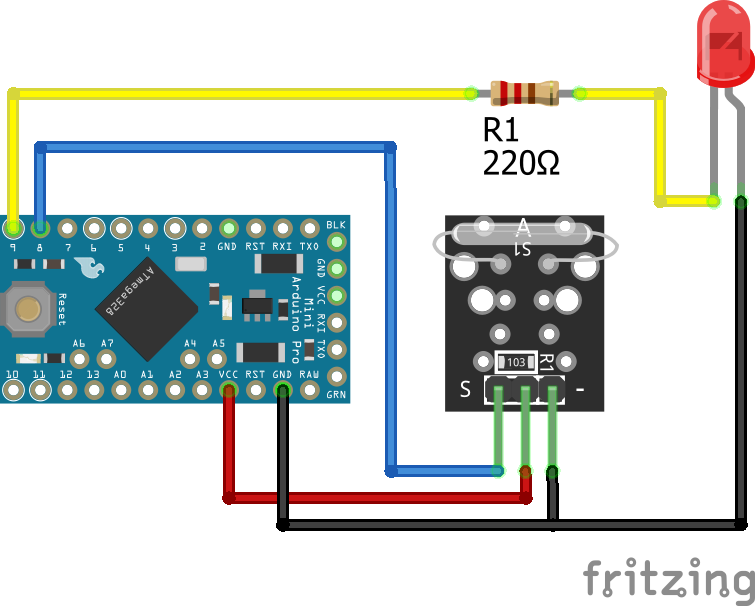
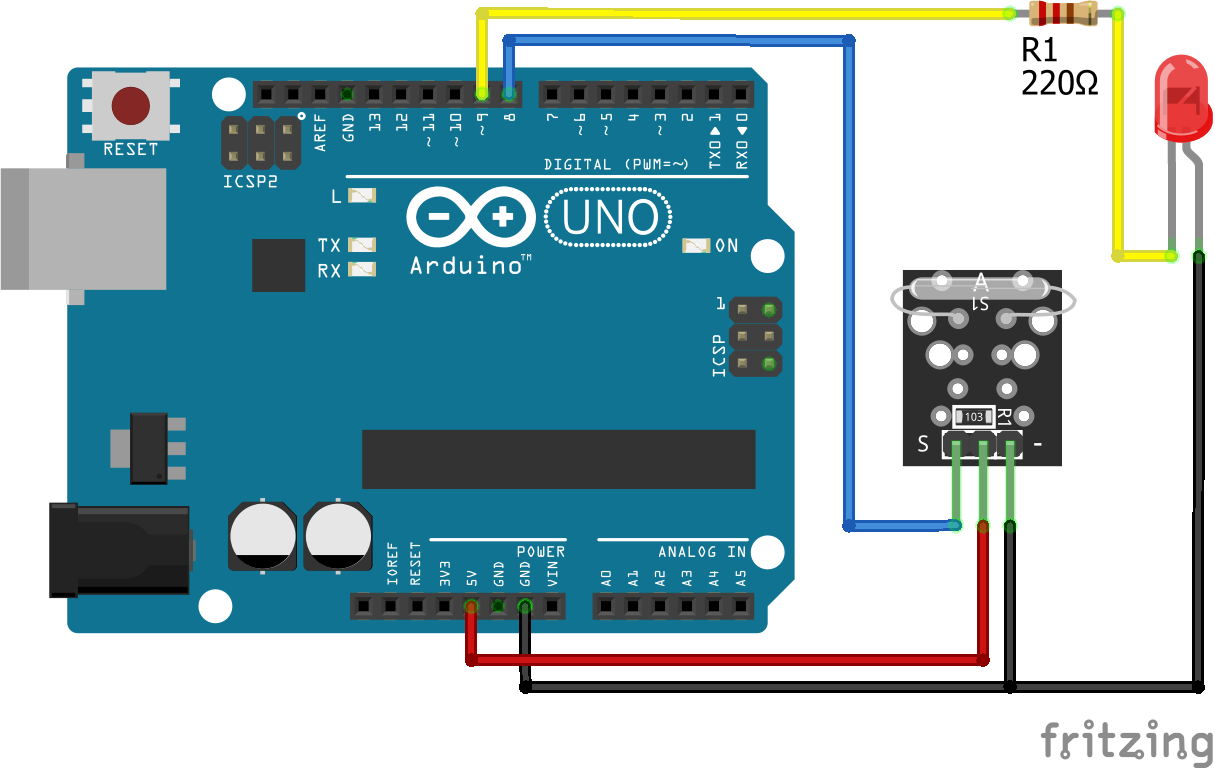
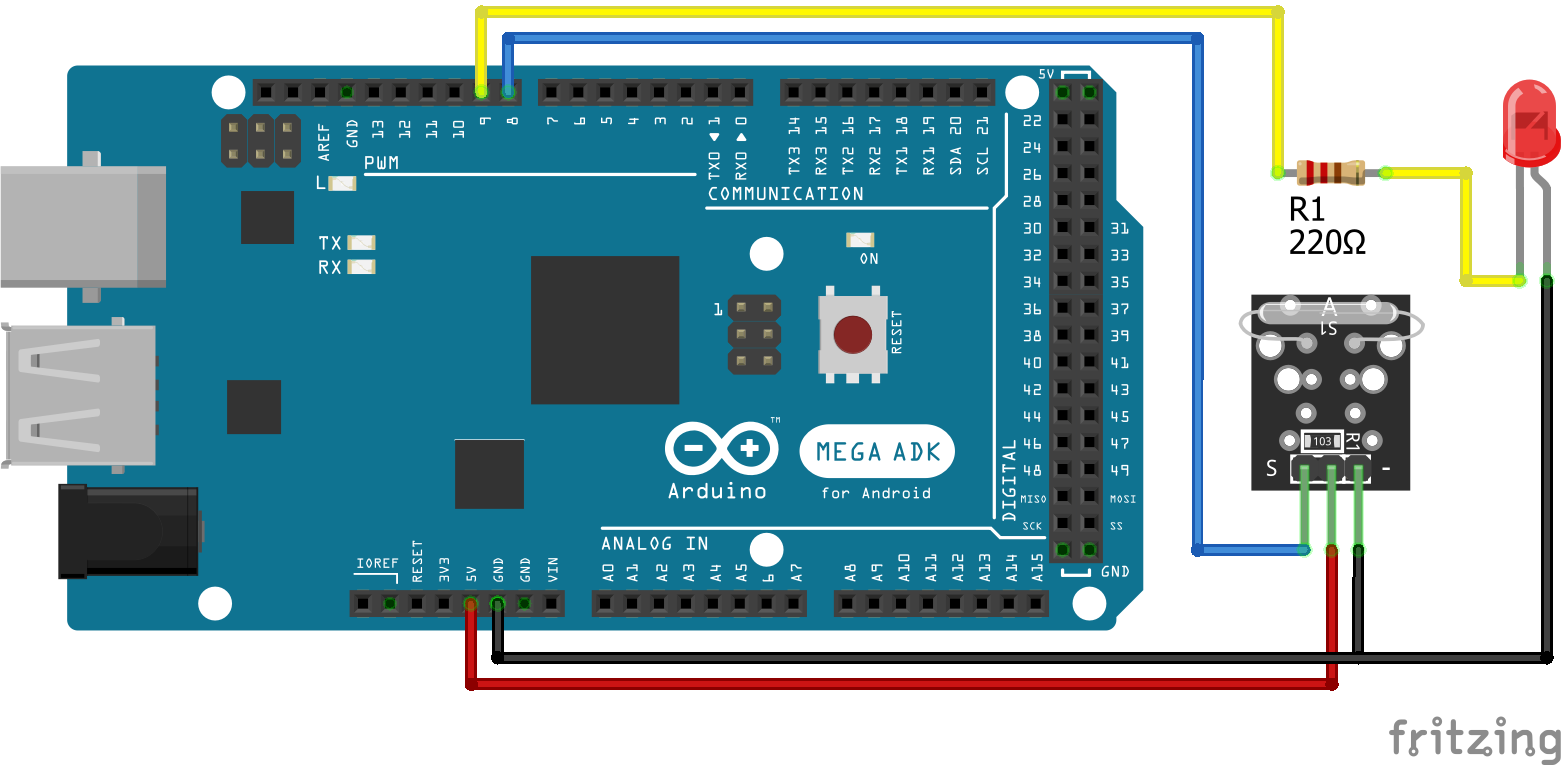
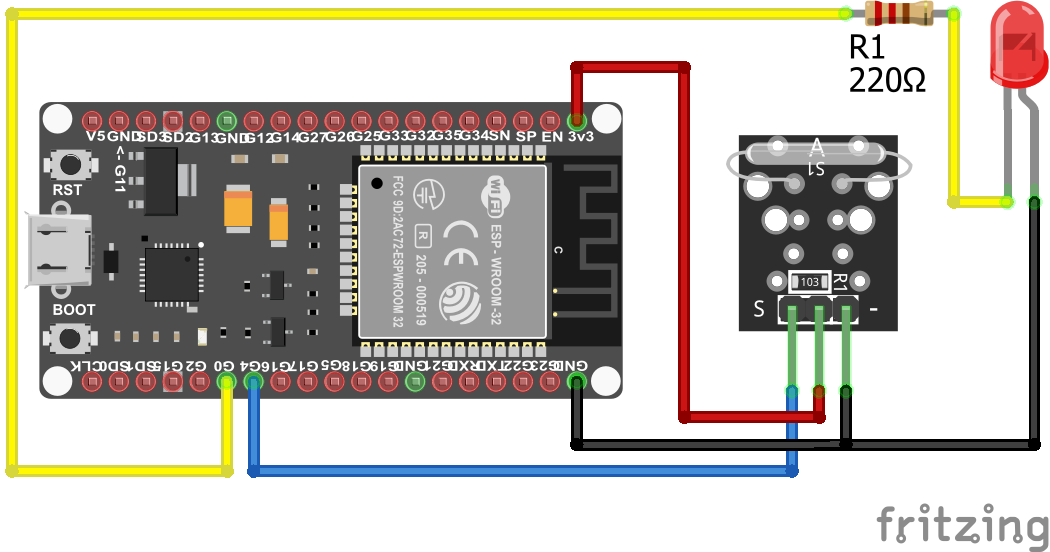
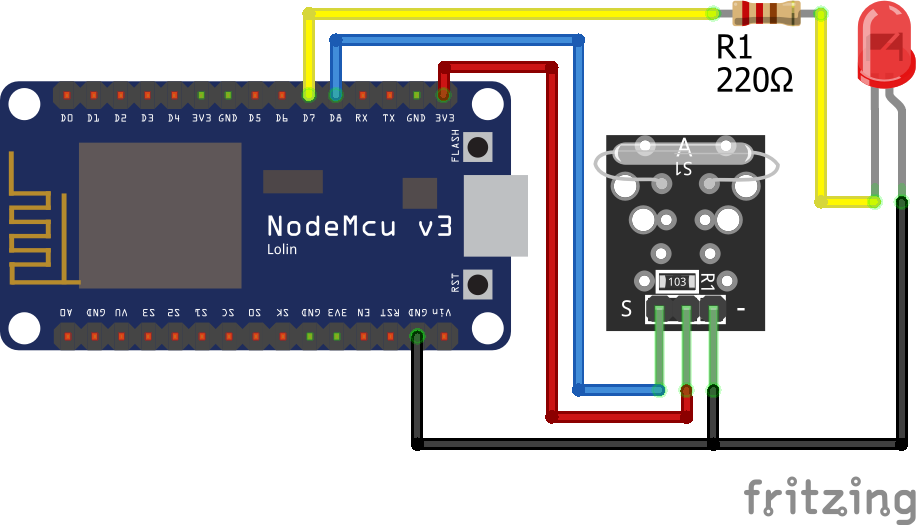
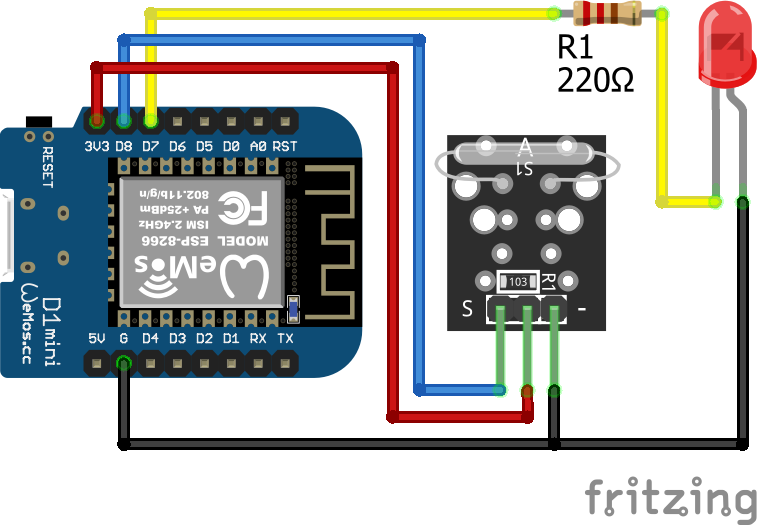
KY-021 Digital Connection
After the KY-025 we also want to test the KY-021 reed switch that has only a digital output and no build in LED. Therefor I use an external LED with a resistor of 220 ohm in series to visualize that the threshold is exceeded. The LED is connected to a digital pin and ground. Therefore we can use this digital pin to turn the LED on and off.
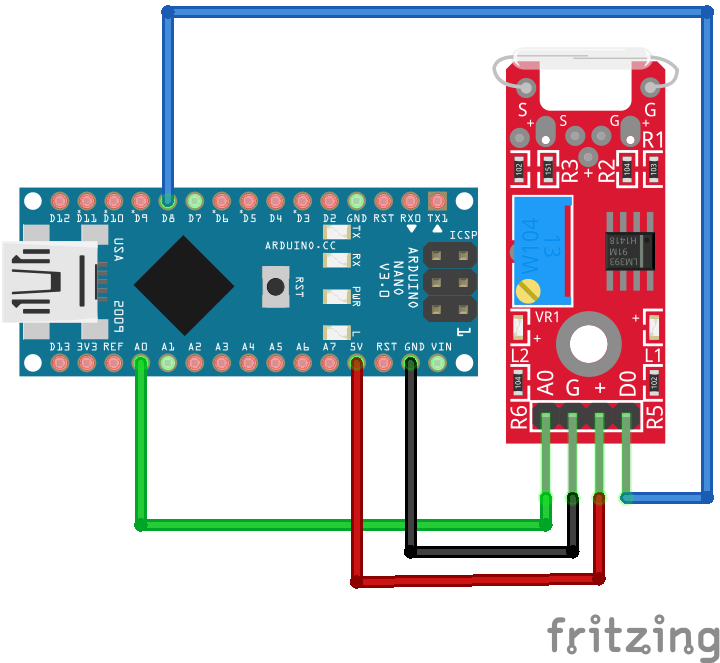
The following pictures show the wiring between the KY-021 and the Arduino, ESP8266 or ESP32 microcontroller boards.
Most of the program code that we use for the KY-021 reed switch is the same as for the KY-025. We only have to delete the parts for the analog connection and add the code that the external LED is turned on and off depending on the strength of the magnetic field.
The following section shows the Arduino code for the KY-021 that you can use with Arduino, ESP8266 or ESP32 microcontrollers.
// for Arduino microcontroller
int ledPin = 7;
int digitalPin = 8;
// for ESP8266 microcontroller
//int ledPin = D7;
//int digitalPin = D8;
// for ESP32 microcontroller
//int ledPin = 0;
//int digitalPin = 2;
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int digitalVal = digitalRead(digitalPin);
if (digitalVal == LOW) {
digitalWrite (led, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite (led, LOW);
}
delay(100);
} In this first part of the program, we replaced the analog pin with the pin where the LED is connected. Again, you have to comment and uncomment the first part of the script so that the script matches your microcontroller.
In the setup function we also replace the analog pin with the led pin but because we want to control the LED with the microcontroller and therefore change the status of the digital I/O pin, the LED pin has to be defined as output and not as input. The rest of the setup function is the same like for the KY-025.
In the loop function, first we read the digital value with the digital read function on the previously defined digital pin. To control the LED we use a if function is the following manner:
- If the digital value is 0 (=LOW) the reed switch opens due to the magnetic field. Therefore we turn the LED on
- Otherwise we turn the LED off
At the end of the script we wait for 0.1 seconds and start to read the digital value again in the next iteration of the loop function.
The following video shows how the LED turns on when I get in the near of the KY-021 reed switch.
Conclusion
In this tutorial we learned how a magnetic switch is used to build a security system for doors or windows for example. Moreover we used two different reed switches and showed in different examples the difference between the analog and digital operation mode.
If you have any further questions about reed switches, use the comment section below..
Also if you are interested in active switches, I also wrote a tutorial for these kind of switches where I also dive into the debouncing problem of switches and how to reduce the debouncing. Here is the link to the article.



Leave A Comment